View more
Many of our electronics today rely on batteries, from laptops to phones to smart home appliances to even cars. It’s almost ironic, then, that these critical batteries are also one of the most dangerous things we keep near our bodies, not to mention a hazard to the health of the planet as well. From the way they are made to the unsustainable metals and chemicals they contain, batteries, by nature, seem opposed to life itself.
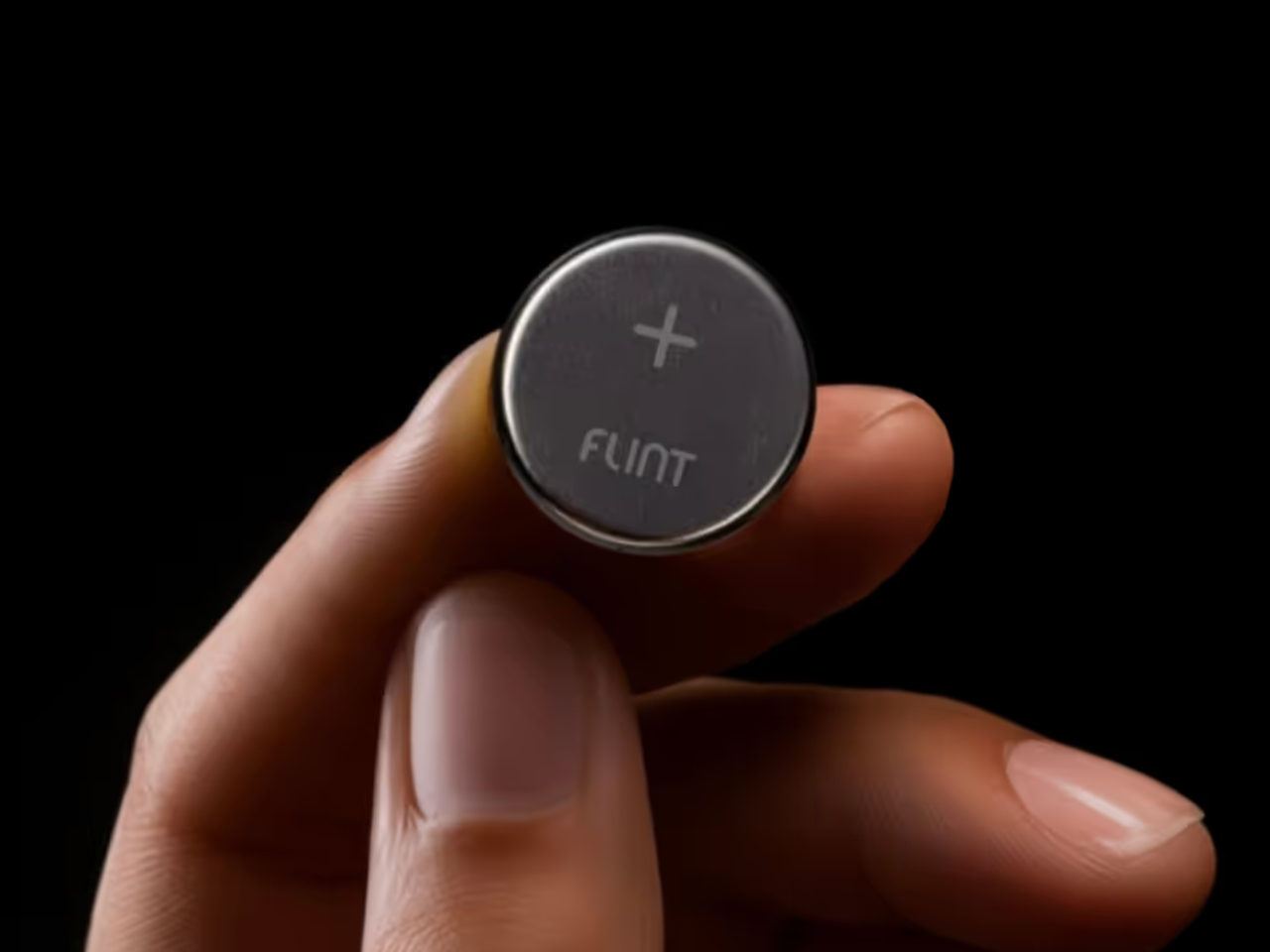
Green energy like solar and wind can go only as far as recharging batteries, but we still need these volatile objects to power devices directly. This innovative battery, however, attempts to reinvent batteries from the ground up to provide true sustainable power to the point that they can even be broken down as compost. Even more intriguing, they’re made of materials you’d least expect to find in batteries: paper and water.
Designer: Flint
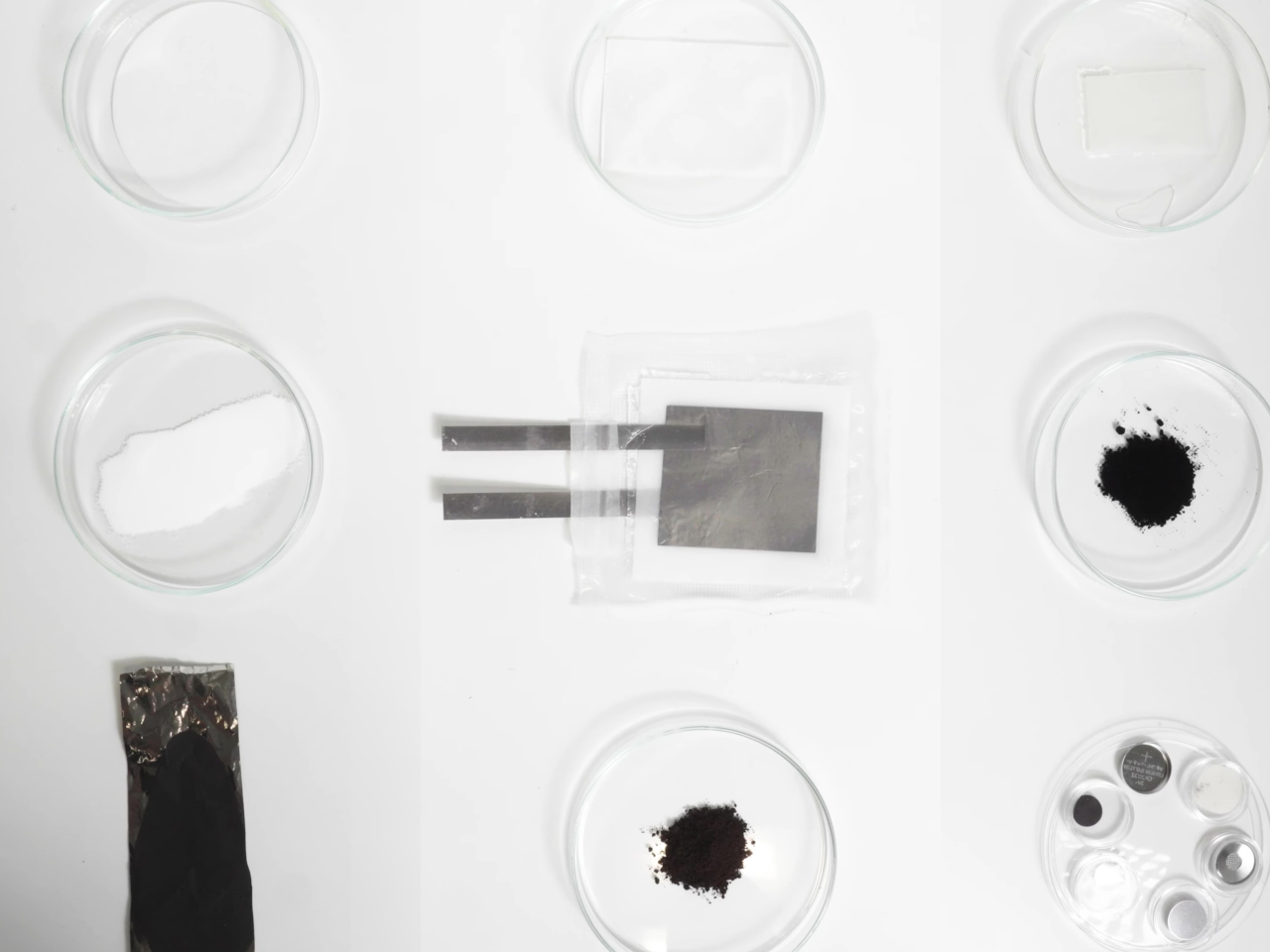


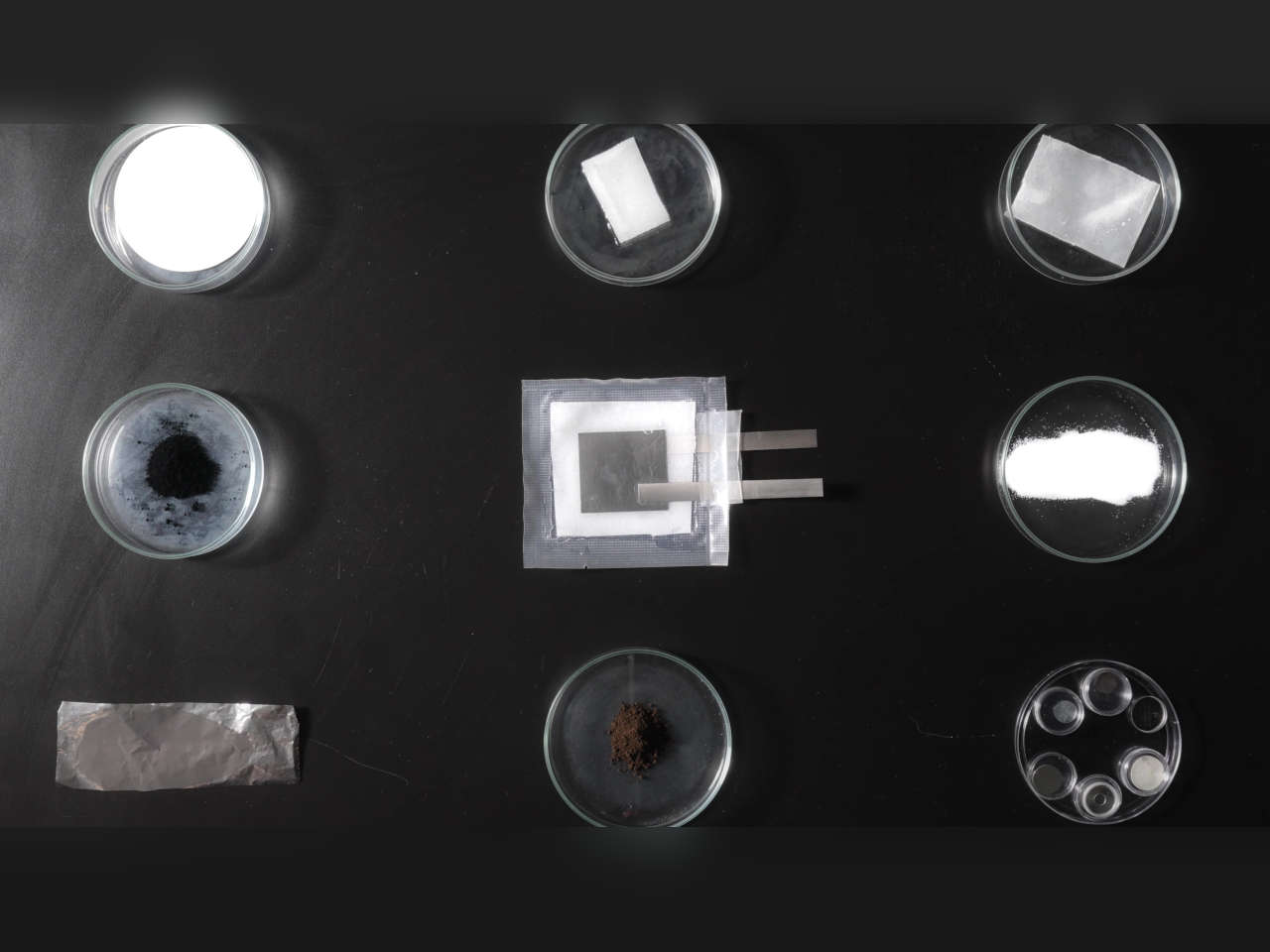
Technically speaking, the batteries aren’t made of the same kind of paper you write on or read from. It actually uses cellulose as the structural backbone and separator of the battery, an abundant material derived from plants and also used in paper, hence the name. As for water, it’s used as the foundation for the electrolytes that actually carry the electrical flow between the zinc-based anode and the manganese-based cathode, both of which are non-reactive, safe, and commonly found everywhere.
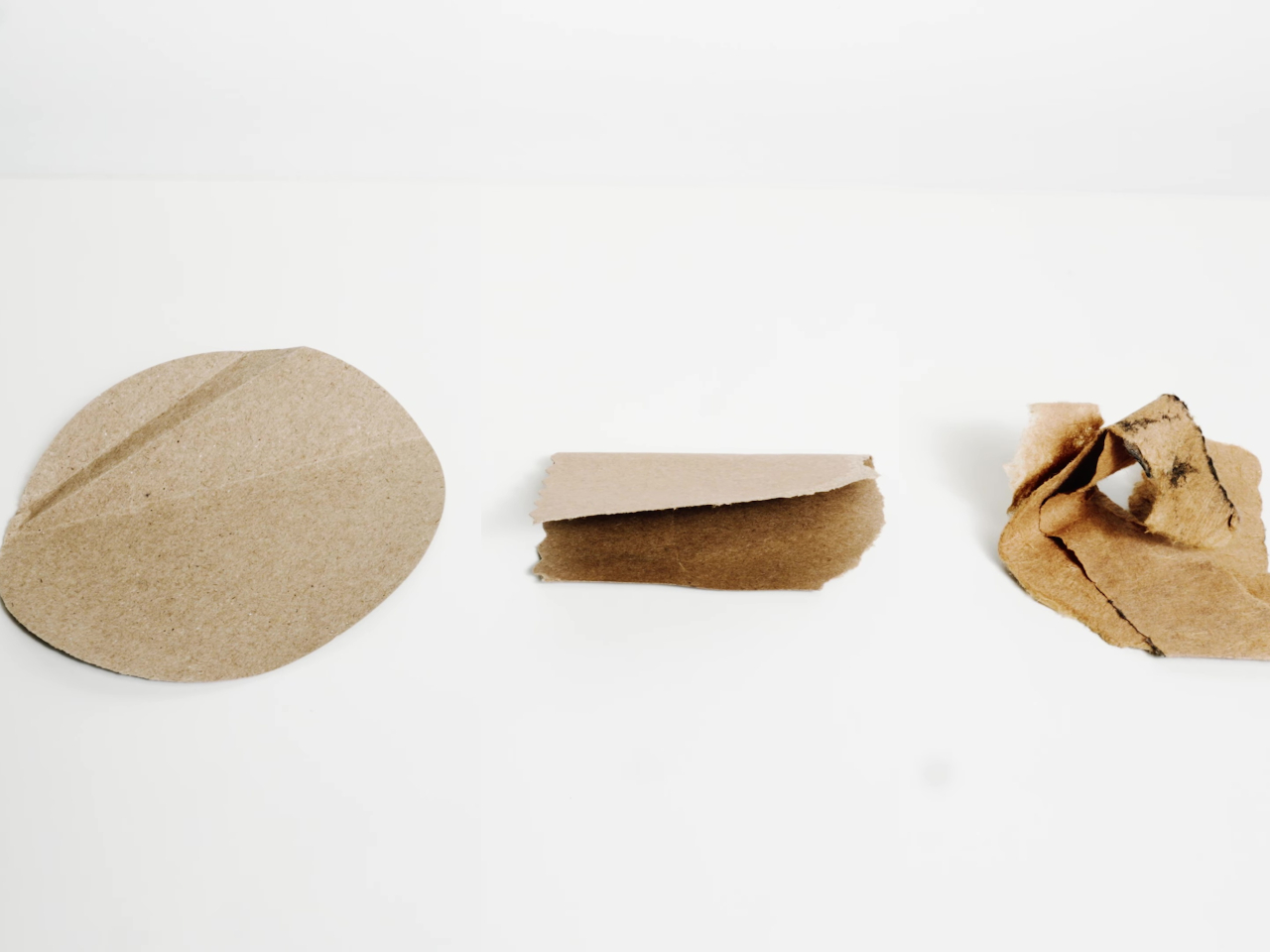
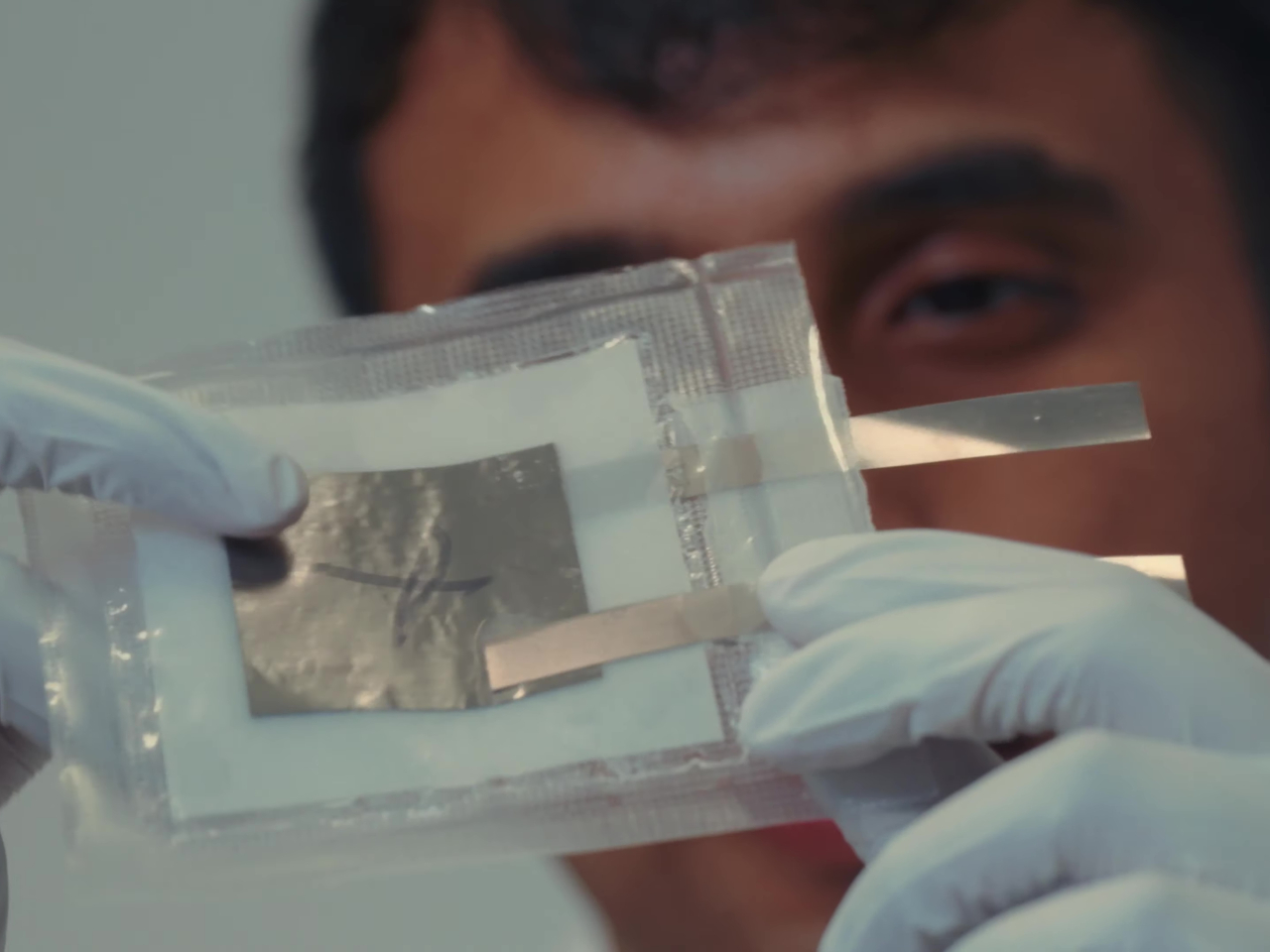


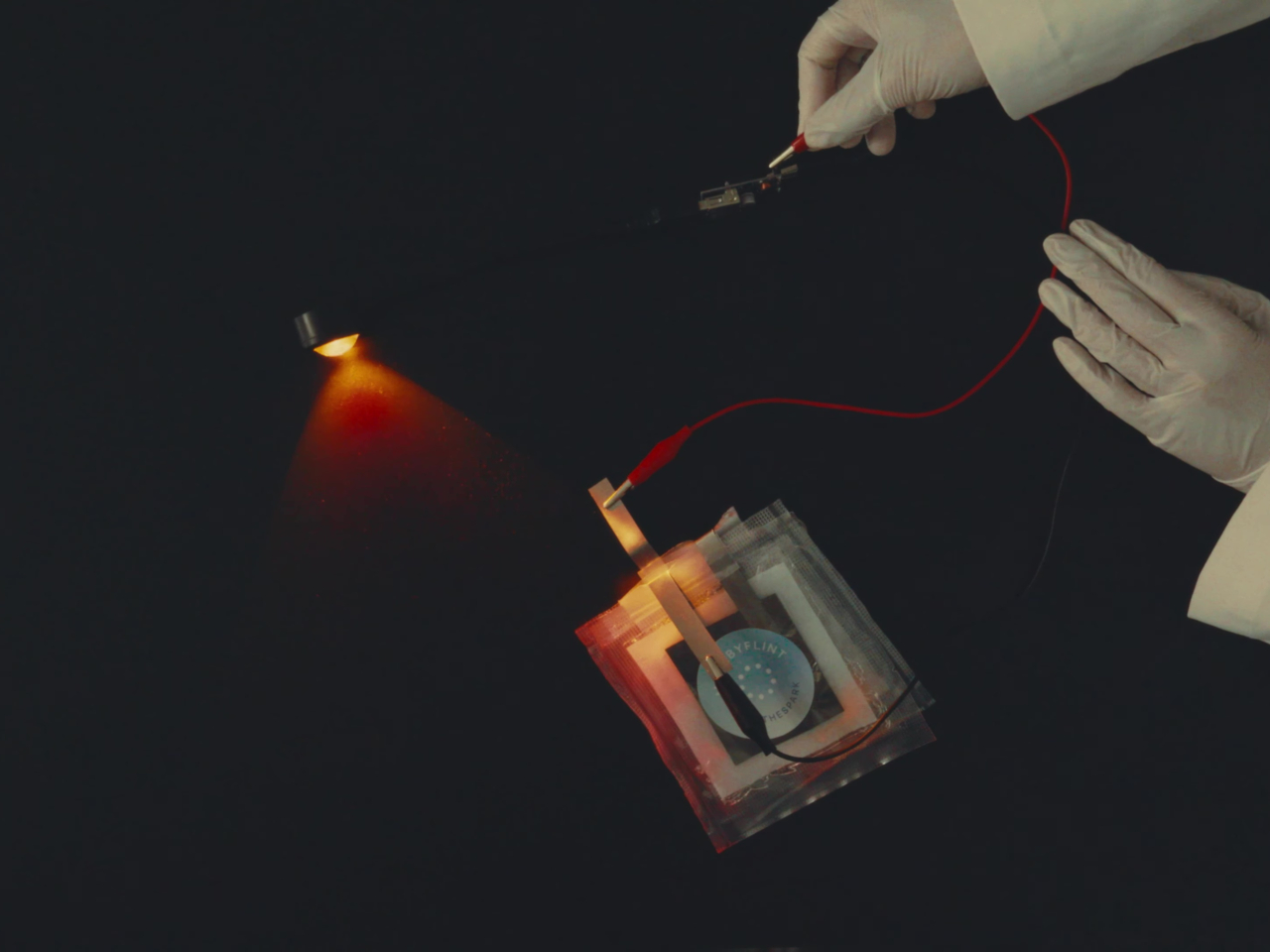
This unusual composition for a battery yields many benefits beyond simply being made of sustainable materials. For one, the battery has unbelievable resilience and can still output power even when cut in half, let alone not explode in your pocket when punctured. It’s also impervious to fire since it uses water-based electrolytes. This practically removes the need for those fancy but complicated and expensive cooling systems in phones and laptops, presuming they get used in those devices. The batteries can also be folded and bent safely, finally realizing the dream of flexible batteries.
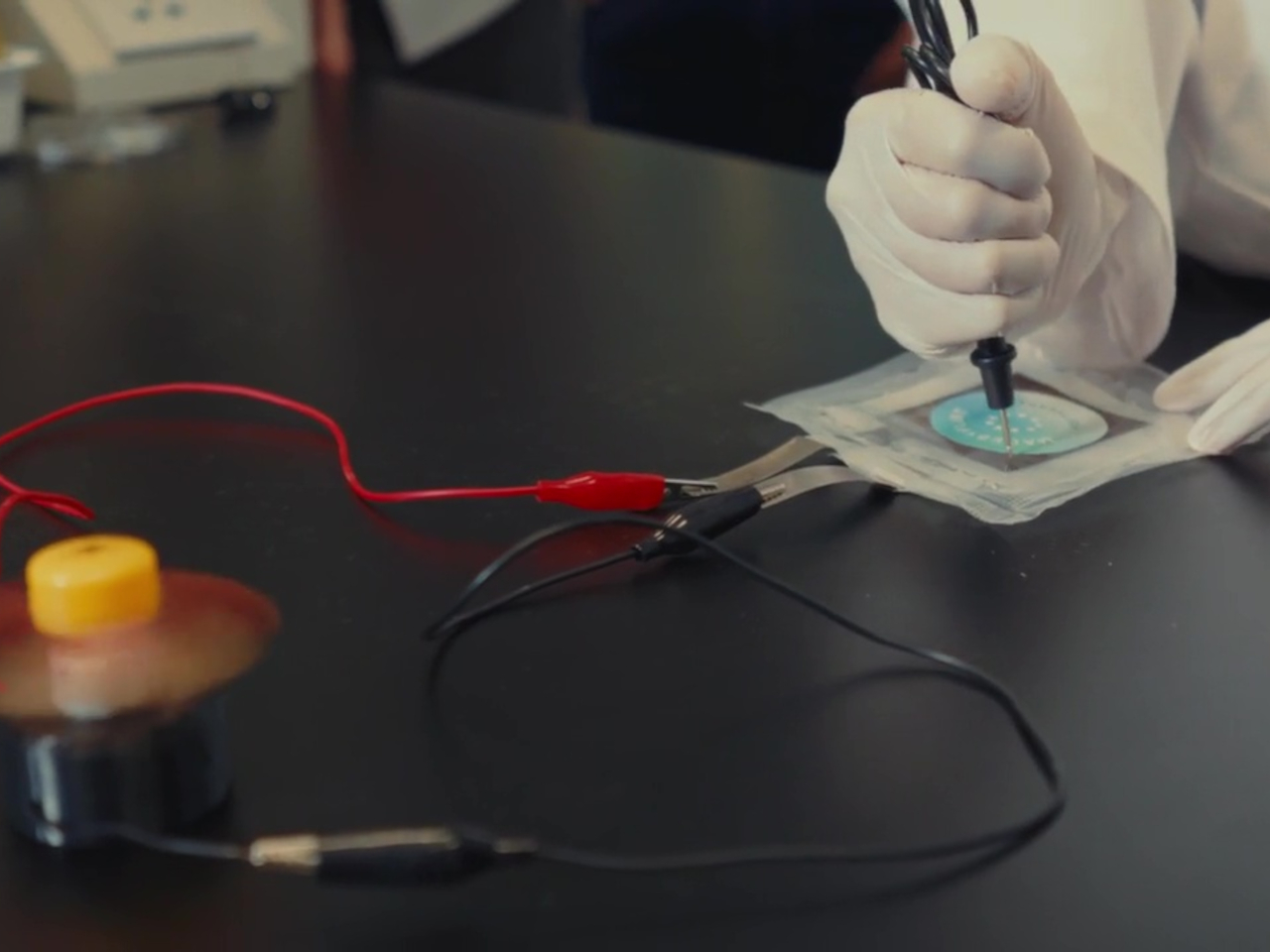
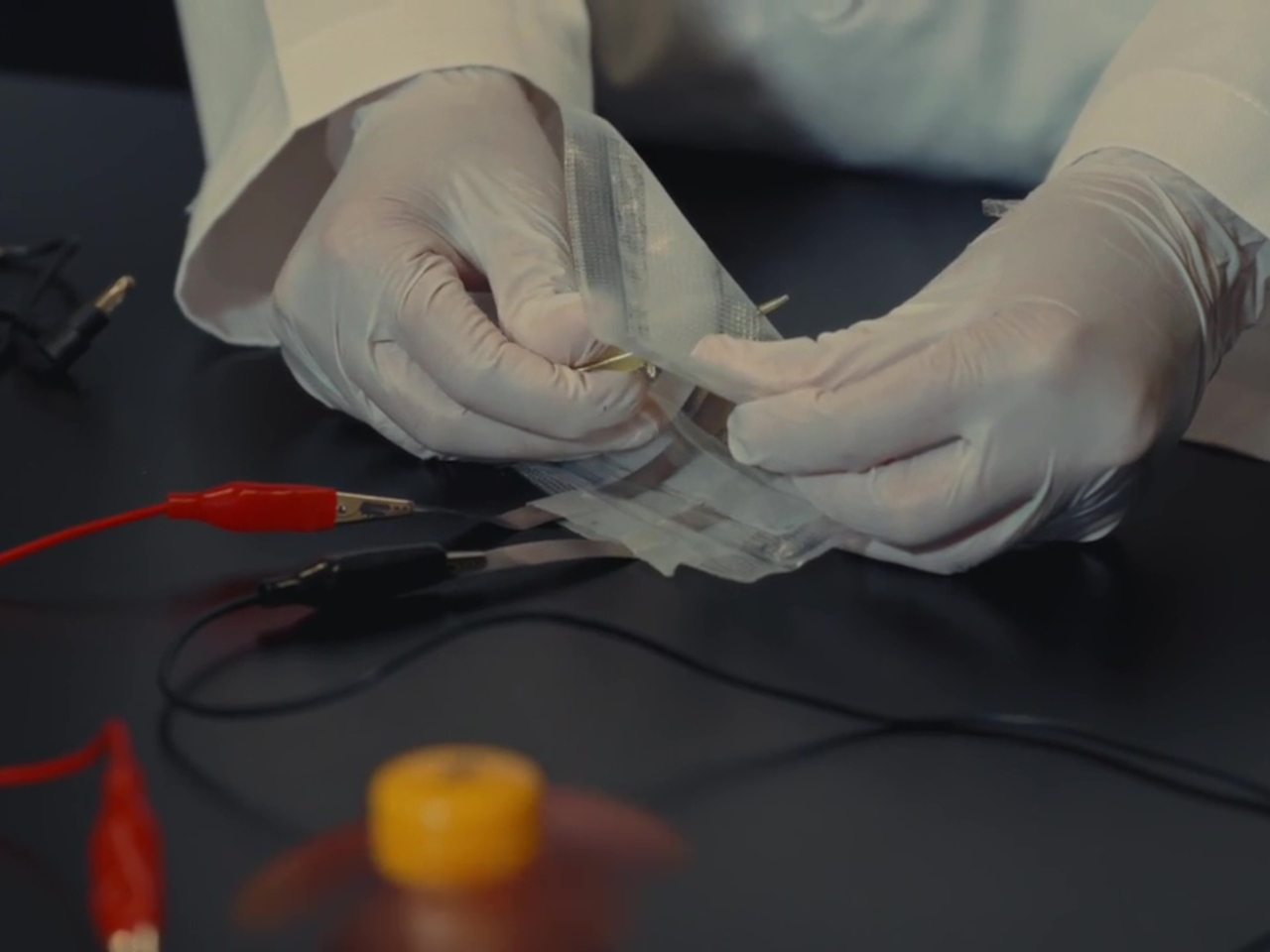
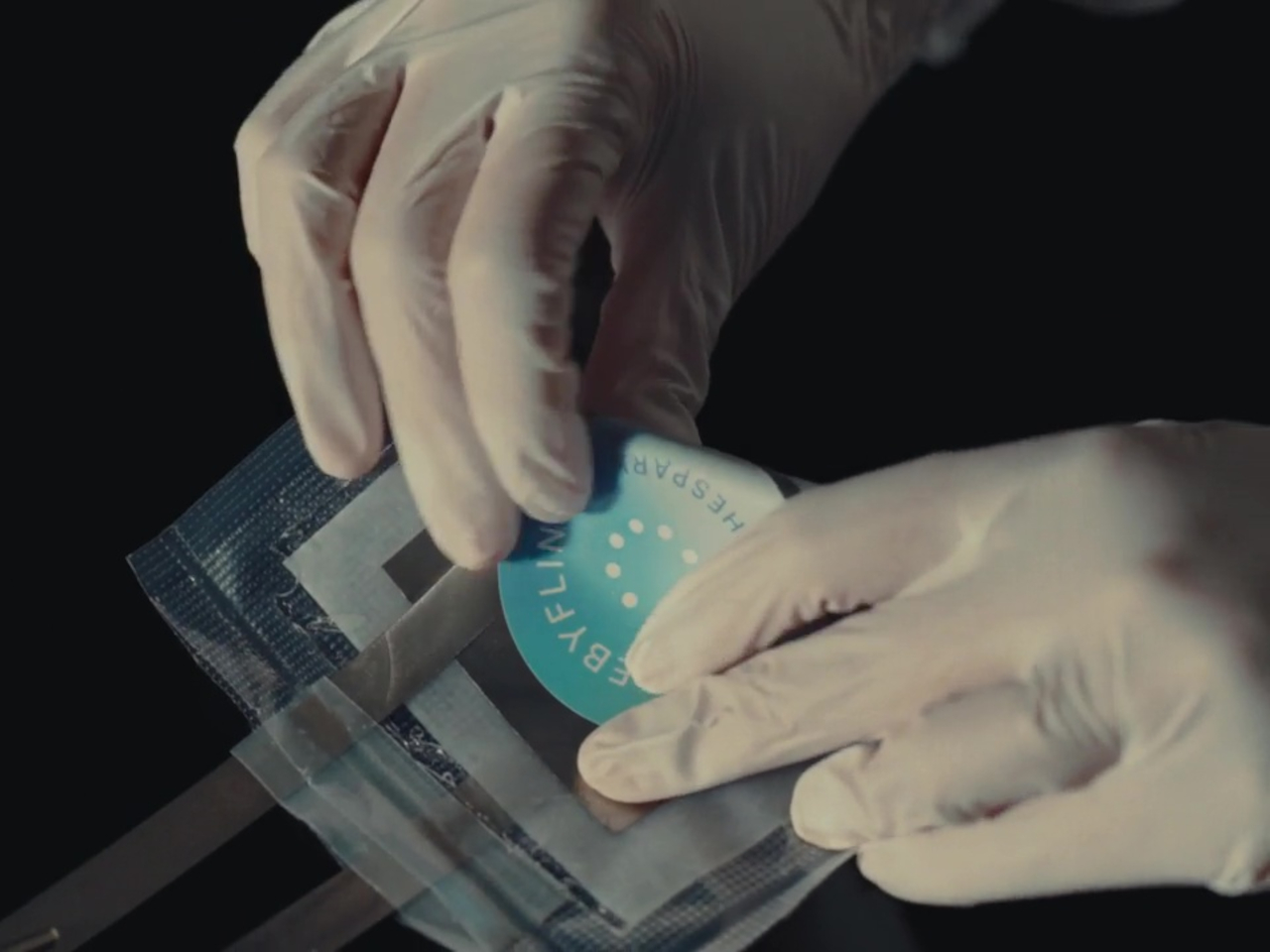
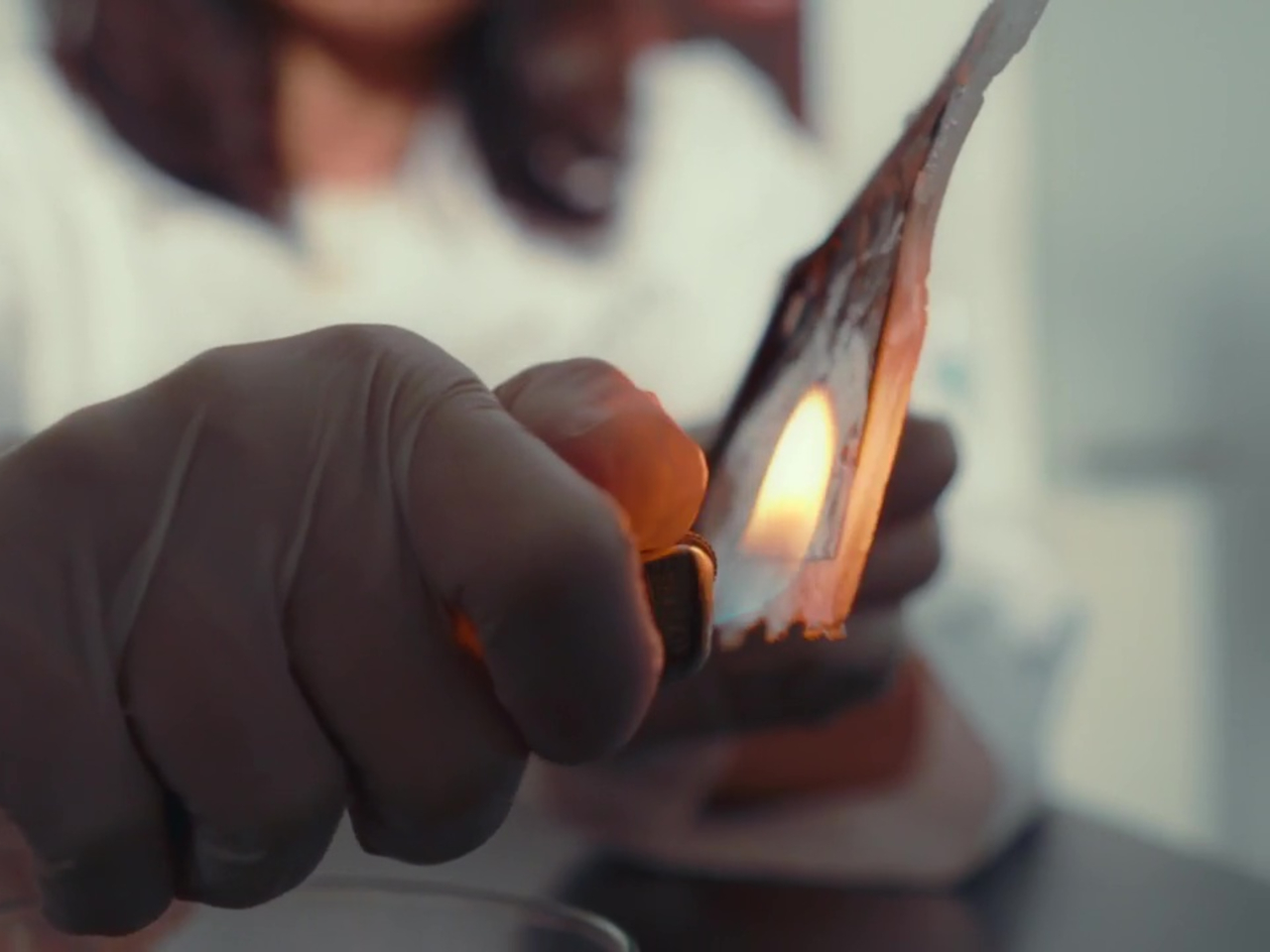




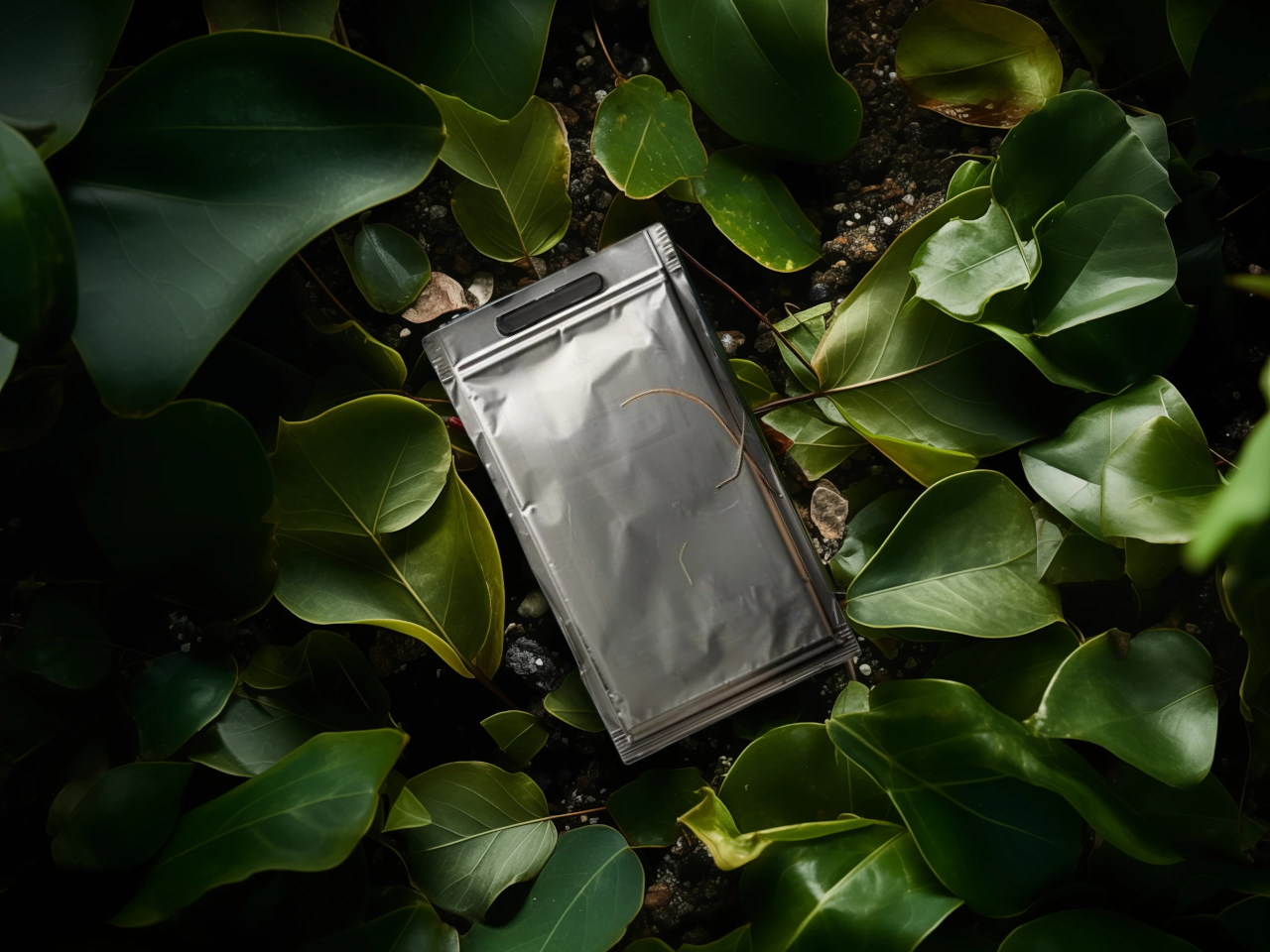
The Flint Paper Batteries are advertised to have the same performance in terms of output and longevity as typical toxic rechargeable batteries. And yes, they’re rechargeable as well. They won’t live forever, though, and when they’ve finally lost their charge for good, simply removing the vacuum-sealed casing starts the natural degradation process that breaks them down into harmless components.
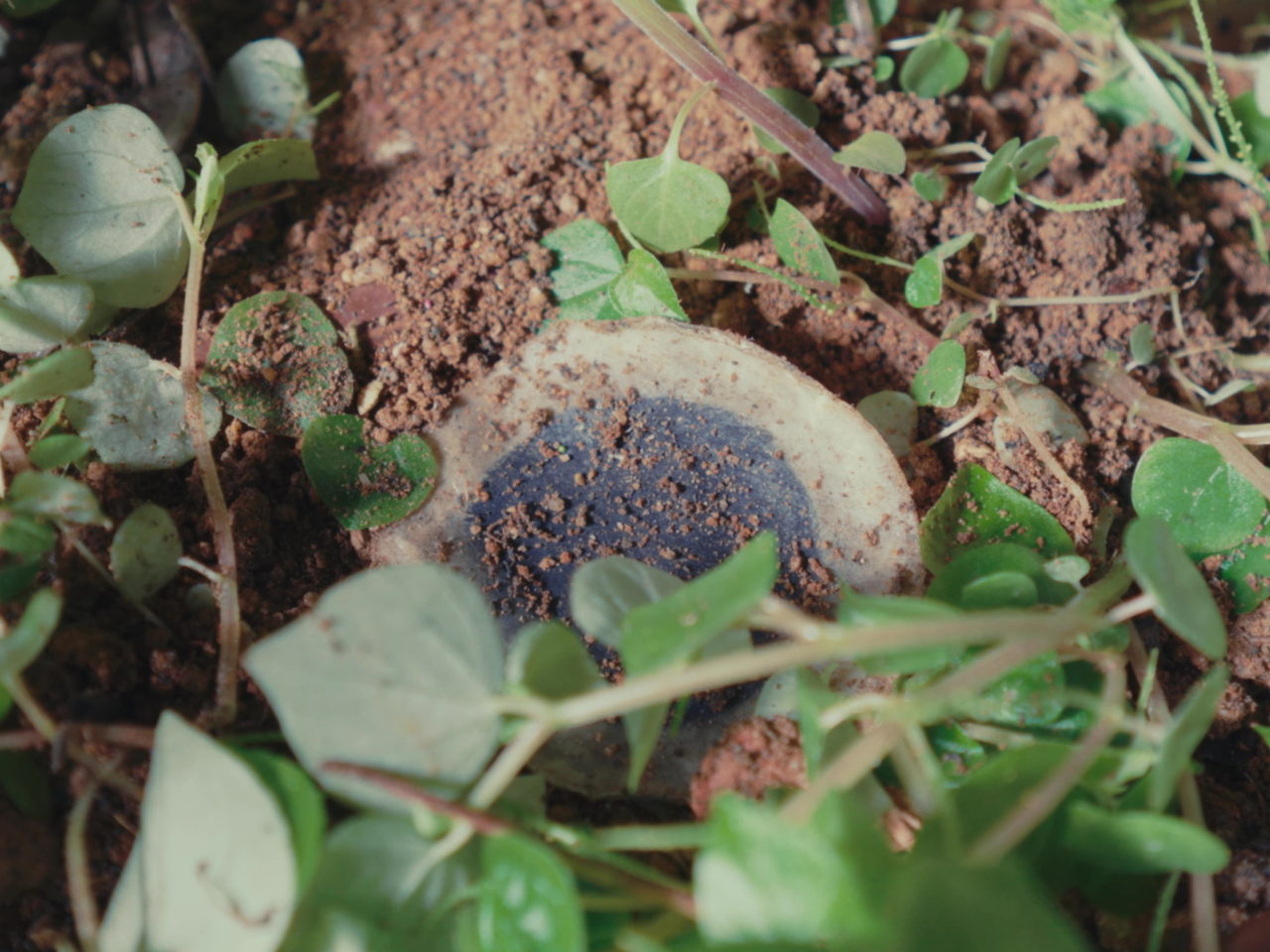

It all sounds idyllic but the technology is not completely ready for mass consumption just yet. One of the biggest hurdles that still needs to be overcome is mass production, and Flint’s creators are planning on using currently existing lithium-ion battery manufacturing processes in order to minimize production and adoption costs. When that happens, we could finally take a major step forward in running not only on green power but also on safe and recyclable batteries as well.